Post time: Nov-13-2023
Harnessing Power: Unveiling the Pneumatic Actuator
Pneumatic actuators play a crucial role in various industries, providing a dynamic and efficient means of converting energy into mechanical motion. These devices, powered by compressed air, find applications in automation, manufacturing, and numerous other fields. In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of pneumatic actuators, exploring their functionality, types, and applications.
Understanding Pneumatic Actuators
1. Basics of Operation
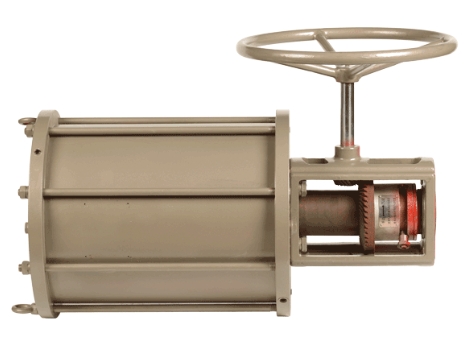
At its core, a pneumatic actuator is a device that converts energy from compressed air into mechanical motion. Compressed air, acting as the power source, is directed into the actuator, creating force and movement. Pneumatic actuators are widely appreciated for their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
2. Types of Pneumatic Actuators
a. Pneumatic Cylinders
Pneumatic cylinders, also known as air cylinders, are one of the most common types of pneumatic actuators. They consist of a cylindrical chamber with a piston inside. When compressed air is introduced, the piston moves, generating linear motion. Pneumatic cylinders find applications in various tasks, such as lifting, pushing, and pulling.
b. Pneumatic Rotary Actuators
Rotary actuators, as the name suggests, convert compressed air energy into rotational motion. These actuators are suitable for applications that require rotary movement, such as turning valves, opening and closing dampers, and operating rotating machinery.
3. Components of a Pneumatic Actuator
a. Cylinder
The cylinder is a crucial component of a pneumatic actuator, serving as the housing for the piston or rotary mechanism. It provides the necessary structure for the actuator to generate motion.
b. Piston
In pneumatic cylinders, the piston is the movable component inside the cylinder. When exposed to compressed air, the piston moves, creating linear motion. The design and characteristics of the piston vary based on the specific application.
c. Control Valve
The control valve regulates the flow of compressed air into the actuator. It determines the direction and speed of the actuator's movement. The precise control offered by the valve is essential for achieving accuracy in various applications.
Applications of Pneumatic Actuators
1. Manufacturing and Automation
Pneumatic actuators are extensively used in manufacturing and automation processes. They power a wide range of machinery, including conveyor systems, robotic arms, and assembly line equipment. The rapid and precise movements enabled by pneumatic actuators contribute to increased efficiency in production.
2. Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, where lightweight and efficient components are paramount, pneumatic actuators play a crucial role. They are utilized in applications such as controlling aircraft landing gear, deploying flaps, and managing various movable components.
3. Automotive Systems
Pneumatic actuators are integral to numerous automotive systems, contributing to functions like door locking mechanisms, brake systems, and automated manufacturing processes within the automotive industry.
Advantages of Pneumatic Actuators
1. Cost-Effectiveness
Pneumatic actuators are generally more cost-effective than their hydraulic or electric counterparts. The simplicity of their design and the availability of compressed air contribute to lower overall costs.
2. High Speed and Precision
Pneumatic actuators are known for their high-speed operation and precise control. This makes them suitable for applications where quick and accurate movements are essential.
3. Durability and Reliability
The robust construction of pneumatic actuators ensures durability and reliability in various industrial environments. They can withstand harsh conditions and require minimal maintenance.
Conclusion: Powering Progress with Pneumatics
In conclusion, pneumatic actuators serve as versatile workhorses in the world of automation and manufacturing. Their efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make them a preferred choice for a wide range of applications. From automotive systems to aerospace components, pneumatic actuators play a pivotal role in powering progress across diverse industries.
For further information on pneumatic actuators or to explore our range of automation solutions, please don't hesitate to contact us.