Post time: Jan-15-2024
How Does a Hose Pump Work?
Hose pumps, a type of positive displacement pump, play a crucial role in various industries due to their versatility and reliability. These pumps operate on a unique principle that sets them apart from conventional pumping mechanisms. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of how a hose pump works, exploring its components and the fluid-handling process it employs.
1. The Basics of Positive Displacement Pumps
1.1 Introduction to Positive Displacement:
Hose pumps fall under the category of positive displacement pumps, a type known for delivering a fixed amount of fluid with each revolution of the pump's mechanism. This contrasts with dynamic pumps, such as centrifugal pumps, which rely on velocity and kinetic energy for fluid transfer.
1.2 Advantages of Positive Displacement:
Positive displacement pumps, including hose pumps, are favored for their ability to handle viscous fluids, offer precise control over flow rates, and maintain consistent pressure. These features make them suitable for a wide range of applications across industries.
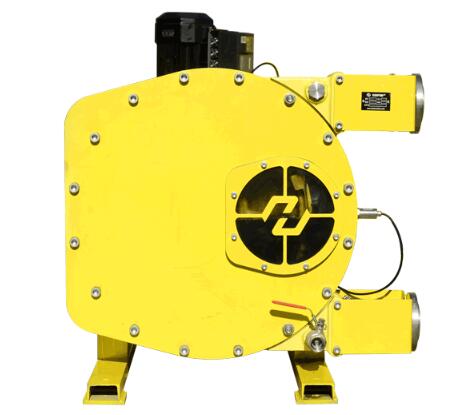
2. Key Components of a Hose Pump
2.1 Hose:
The primary component of a hose pump is, unsurprisingly, the hose itself. Typically made of reinforced rubber or other flexible materials, the hose undergoes repeated compression and relaxation during the pumping process.
2.2 Rotor:
The hose is compressed by a rotor, also known as a shoe or roller, which moves along the length of the hose. This movement creates a squeezing action, forcing the fluid within the hose to move in the desired direction.
2.3 Housing:
The housing, or casing, encloses the hose and rotor, providing structural support and preventing fluid from escaping during the pumping cycle. The housing also contributes to the creation of a vacuum that draws the fluid into the hose.
3. The Peristaltic Pumping Principle
3.1 Squeezing and Releasing:
The hose pump operates on the peristaltic pumping principle, named after the process of peristalsis seen in natural biological systems. In a hose pump, peristaltic action involves the squeezing and releasing of the flexible hose to create a positive displacement of the fluid.
3.2 Fluid Movement:
As the rotor compresses the hose, the fluid is forced to move along the hose in the direction dictated by the pump design. The squeezing action results in a steady flow of fluid, making it particularly effective for applications requiring accurate dosing and metering.
4. Versatility in Fluid Handling
4.1 Handling Viscous Fluids:
One of the notable advantages of hose pumps is their ability to handle fluids with varying viscosities. The peristaltic pumping action is well-suited for viscous liquids, making these pumps ideal for applications where maintaining the integrity of the fluid is crucial.
4.2 Gentle Handling of Shear-Sensitive Materials:
The gentle squeezing action of hose pumps makes them suitable for handling shear-sensitive materials. Industries dealing with delicate substances, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing, benefit from the non-shearing nature of hose pump operations.
5. Maintenance and Longevity
5.1 Simple Maintenance:
Hose pumps are known for their simplicity, which extends to maintenance procedures. Replacing the hose, the primary wear component, is a straightforward task that can be accomplished with minimal downtime.
5.2 Extended Service Life:
The design of hose pumps, with the hose as the primary wearing part, contributes to their extended service life. Routine inspections and timely hose replacements ensure the continued efficiency and reliability of these pumps.
Conclusion: A Reliable Fluid Handling Solution
Understanding how a hose pump works unveils a pumping mechanism that combines simplicity with precision. The peristaltic pumping principle, harnessed through the compression and relaxation of a flexible hose, allows these pumps to cater to a diverse range of industries and fluid-handling needs.
For high-quality hose pumps or more information on their applications and advantages, contact us. As a trusted supplier, we offer a range of pumping solutions designed to meet the specific requirements of various industries. Elevate your fluid handling processes with a reliable supplier committed to quality and innovation.